Rubinstein-Taybi 2 associated to novel EP300 mutations: deepening the clinical and genetic spectrum, BMC Medical Genetics
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
Background Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome (RSTS) is a rare autosomal dominant neurodevelopmental disorder characterized by broad thumbs and halluces. RSTS is caused by mutations in CREBBP and in EP300 genes in 50–60% and 8%, respectively. Up to now, 76 RSTS-EP300 patients have been described. We present the clinical and molecular characterization of a cohort of RSTS patients carrying EP300 mutations. Methods Patients were selected from a cohort of 72 individuals suspected of RSTS after being negative in CREBBP study. MLPA and panel-based NGS EP300 were performed. Results Eight patients were found to carry EP300 mutations. Phenotypic characteristics included: intellectual disability (generally mild), postnatal growth retardation, infant feeding problems, psychomotor and language delay and typical facial dysmorphisms (microcephaly, downslanting palpebral fissures, columella below the alae nasi, and prominent nose). Broad thumbs and/or halluces were common, but angulated thumbs were only found in two patients. We identified across the gene novel mutations, including large deletion, frameshift mutations, nonsense, missense and splicing alterations, confirming de novo origin in all but one (the mother, possibly underdiagnosed, has short and broad thumbs and had learning difficulties). Conclusions The clinical evaluation of our patients corroborates that clinical features in EP300 are less marked than in CREBBP patients although it is difficult to establish a genotype-phenotype correlation although. It is remarkable that these findings are observed in a RSTS-diagnosed cohort; some patients harbouring EP300 mutations could present a different phenotype. Broadening the knowledge about EP300-RSTS phenotype may contribute to improve the management of patients and the counselling to the families.

PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: A Model of Epigenetic Disorder
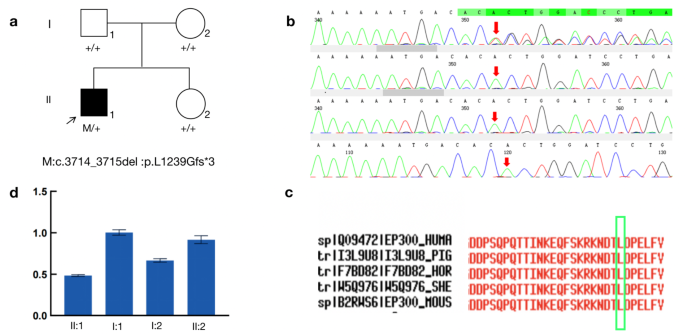
De novo variation in EP300 gene cause Rubinstein-Taybi syndrome 2 in a Chinese family with severe early-onset high myopia, BMC Medical Genomics
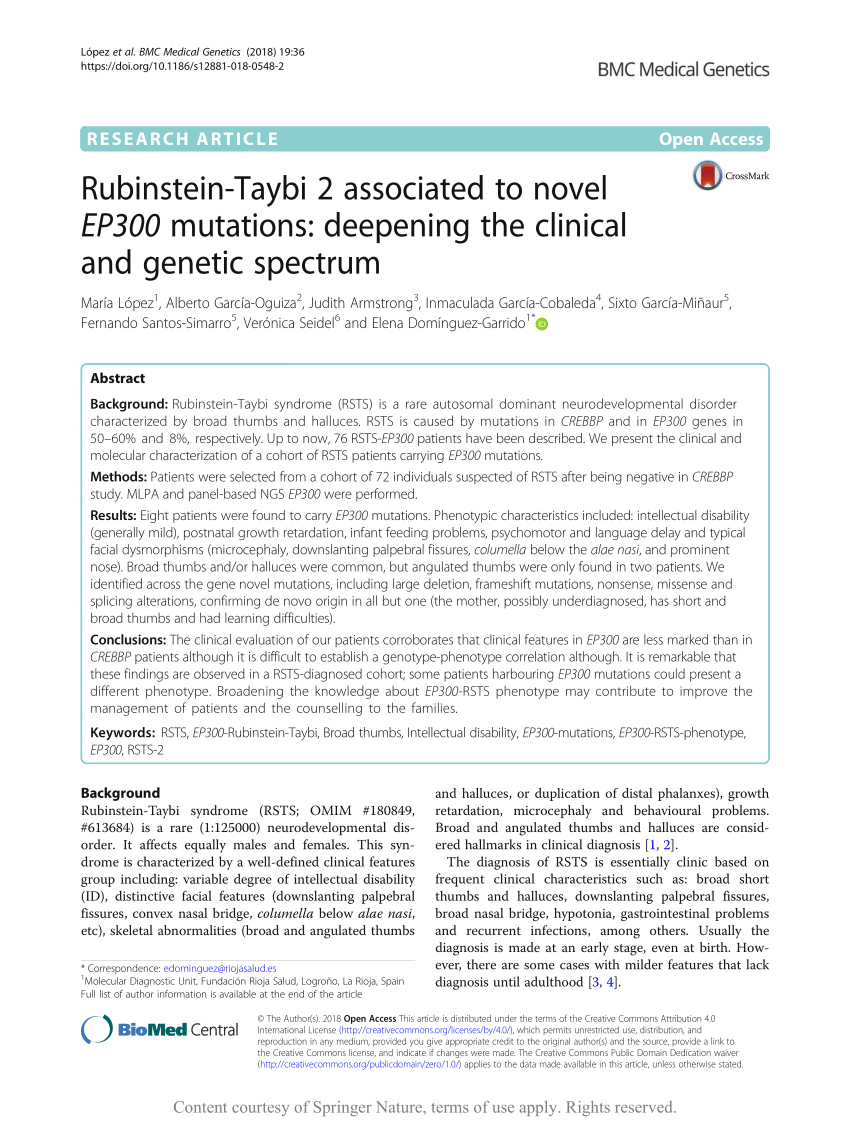
(PDF) Rubinstein-Taybi 2 associated to novel EP300 mutations: Deepening the clinical and genetic spectrum

Genetic Heterogeneity in Rubinstein-Taybi Syndrome: Mutations in Both the CBP and EP300 Genes Cause Disease - ScienceDirect
Frontiers Genetic Diagnosis of Rubinstein–Taybi Syndrome With Multiplex Ligation-Dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) and Whole-Exome Sequencing (WES): Case Series With a Novel CREBBP Variant

Rubinstein–Taybi syndrome - Wikipedia
Genes, Free Full-Text
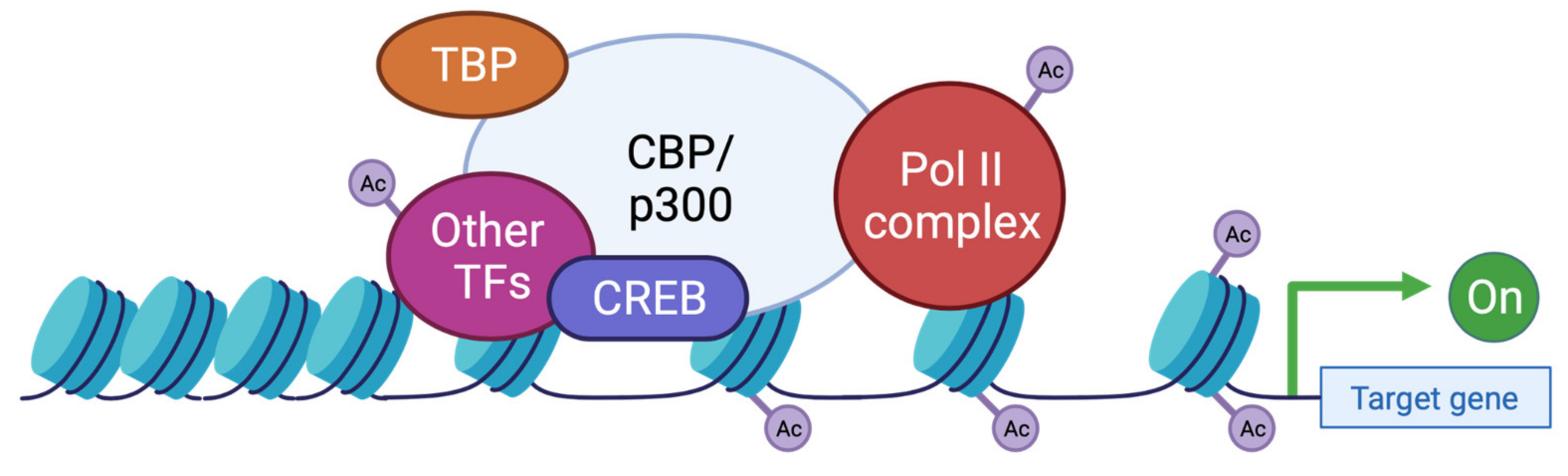
Genes, Free Full-Text

Exon deletions of the EP300 and CREBBP genes in two children with Rubinstein -Taybi syndrome detected by aCGH. - Abstract - Europe PMC

CREBBP and EP300 mutation spectrum.
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)




/s.glbimg.com/po/tt2/f/original/2016/06/07/ps4-fabricado1_copy.jpg)

