Browning of the white adipose tissue regulation: new insights into
Por um escritor misterioso
Descrição
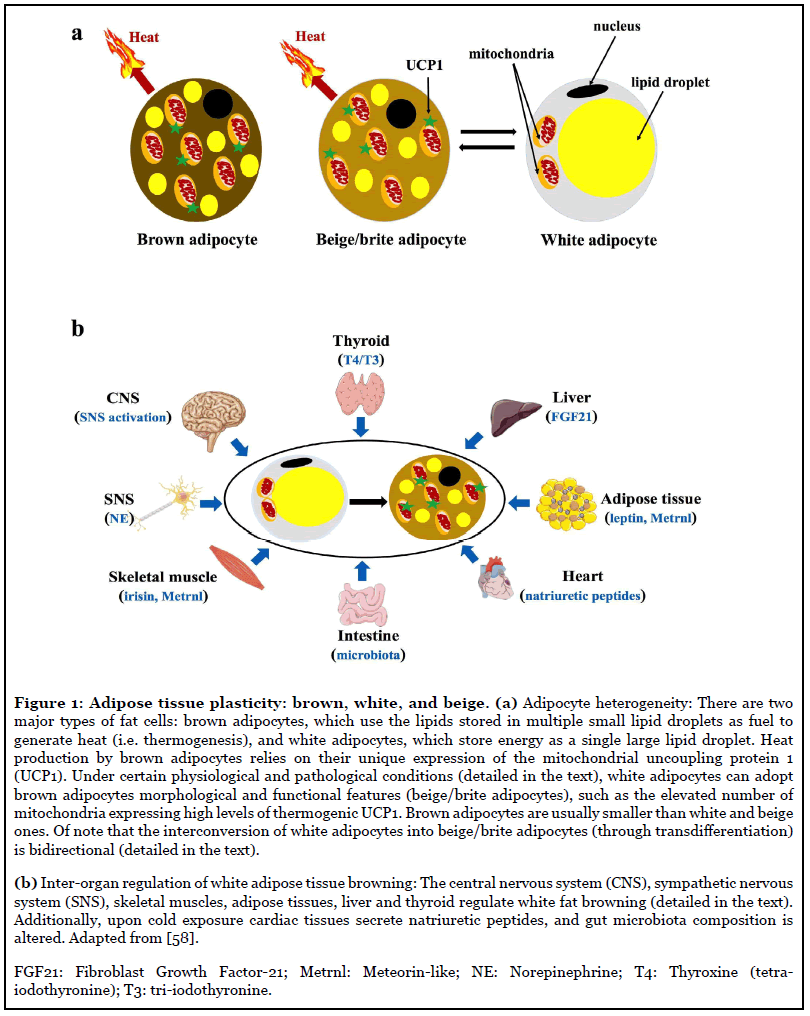
Adipose tissues are dynamic tissues that play crucial physiological roles in maintaining health and homeostasis. Although white adipose tissue and brown adipose tissue are currently considered key endocrine organs, they differ functionally and morphologically. The existence of the beige or brite adipocytes, cells displaying intermediary characteristics between white and brown adipocytes, illustrates the plastic nature of the adipose tissue. These cells are generated through white adipose tissue browning, a process associated with augmented non-shivering thermogenesis and metabolic capacity. This process involves the upregulation of the uncoupling protein 1, a molecule that uncouples the respiratory chain from Adenosine triphosphate synthesis, producing heat. β-3 adrenergic receptor system is one important mediator of white adipose tissue browning, during cold exposure. Surprisingly, hyperthermia may also induce beige activation and white adipose tissue beiging. Physical exercising copes with increased levels of specific molecules, including Beta-Aminoisobutyric acid, irisin, and Fibroblast growth factor 21 (FGF21), which induce adipose tissue browning. FGF21 is a stress-responsive hormone that interacts with beta-klotho. The central roles played by hormones in the browning process highlight the relevance of the individual lifestyle, including circadian rhythm and diet. Circadian rhythm involves the sleep–wake cycle and is regulated by melatonin, a hormone associated with UCP1 level upregulation. In contrast to the pro-inflammatory and adipose tissue disrupting effects of the western diet, specific food items, including capsaicin and n-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids, and dietary interventions such as calorie restriction and intermittent fasting, favor white adipose tissue browning and metabolic efficiency. The intestinal microbiome has also been pictured as a key factor in regulating white tissue browning, as it modulates bile acid levels, important molecules for the thermogenic program activation. During embryogenesis, in which adipose tissue formation is affected by Bone morphogenetic proteins that regulate gene expression, the stimuli herein discussed influence an orchestra of gene expression regulators, including a plethora of transcription factors, and chromatin remodeling enzymes, and non-coding RNAs. Considering the detrimental effects of adipose tissue browning and the disparities between adipose tissue characteristics in mice and humans, further efforts will benefit a better understanding of adipose tissue plasticity biology and its applicability to managing the overwhelming burden of several chronic diseases.
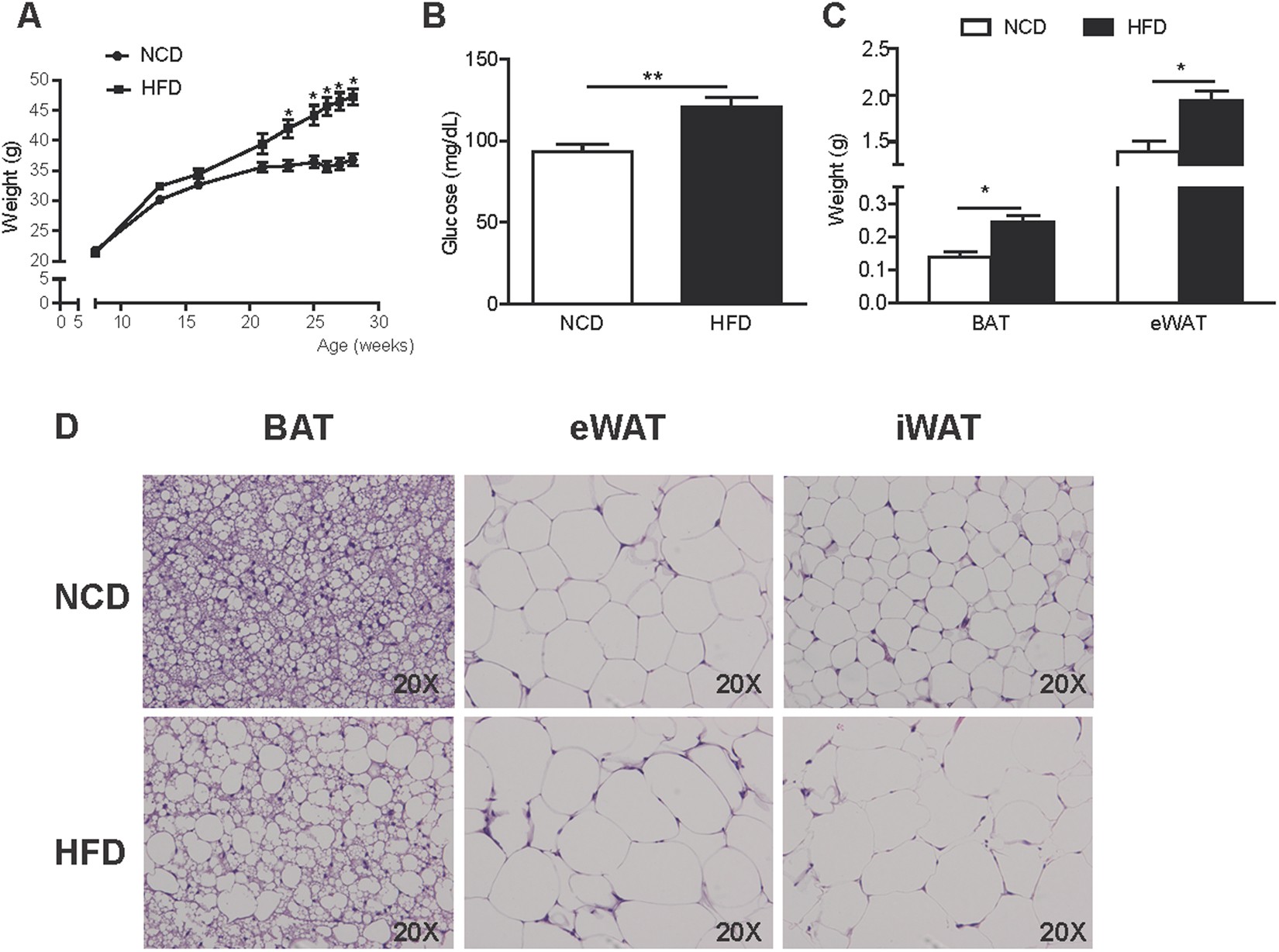
Increased inflammation, oxidative stress and mitochondrial respiration in brown adipose tissue from obese mice

New insights into the role of adipocytes in pancreatic cancer progression: paving the way towards novel therapeutic targets
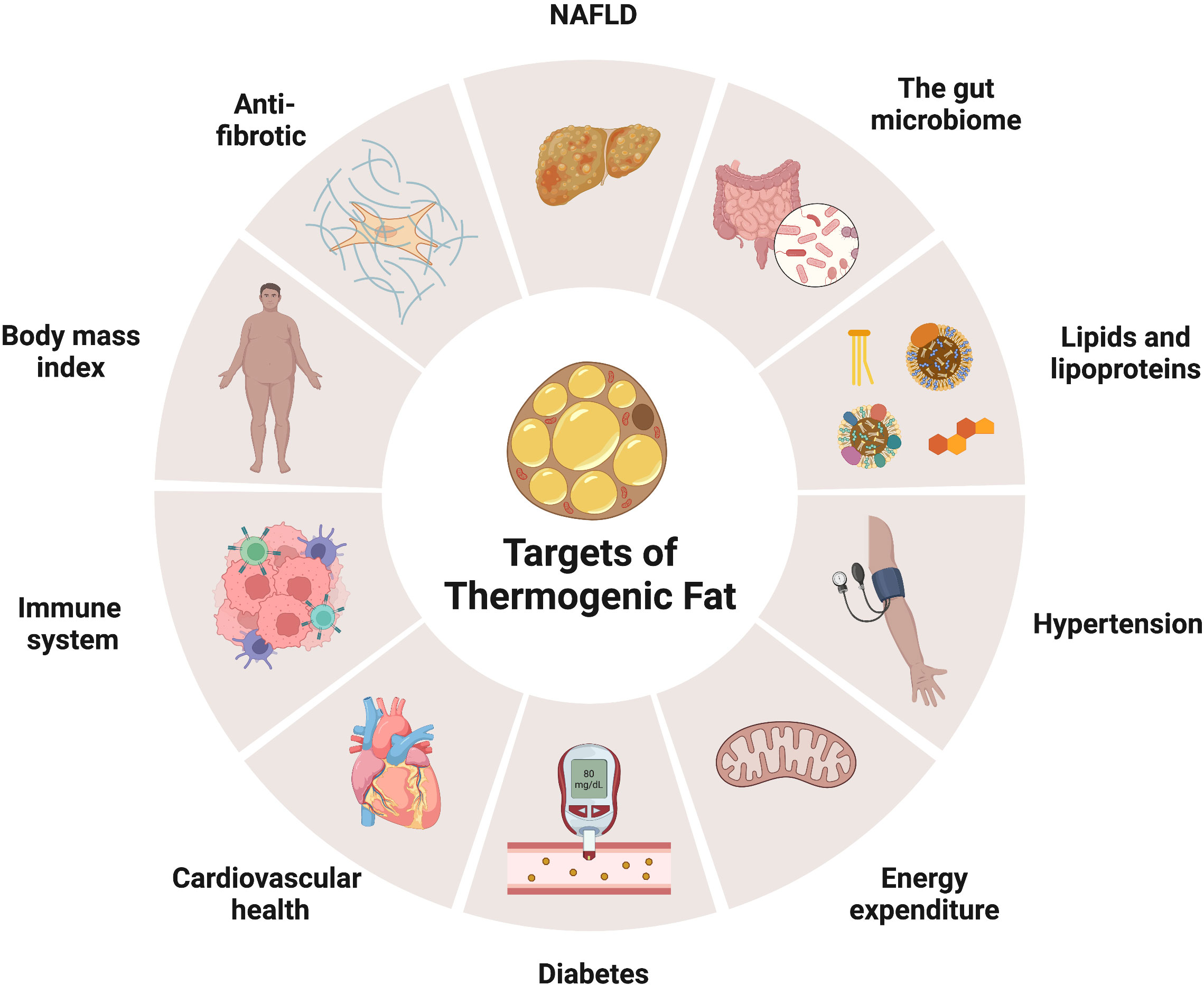
Frontiers Thermogenic adipose tissue in energy regulation and metabolic health
Full article: New insights into adipose tissue VEGF-A actions in the control of obesity and insulin resistance
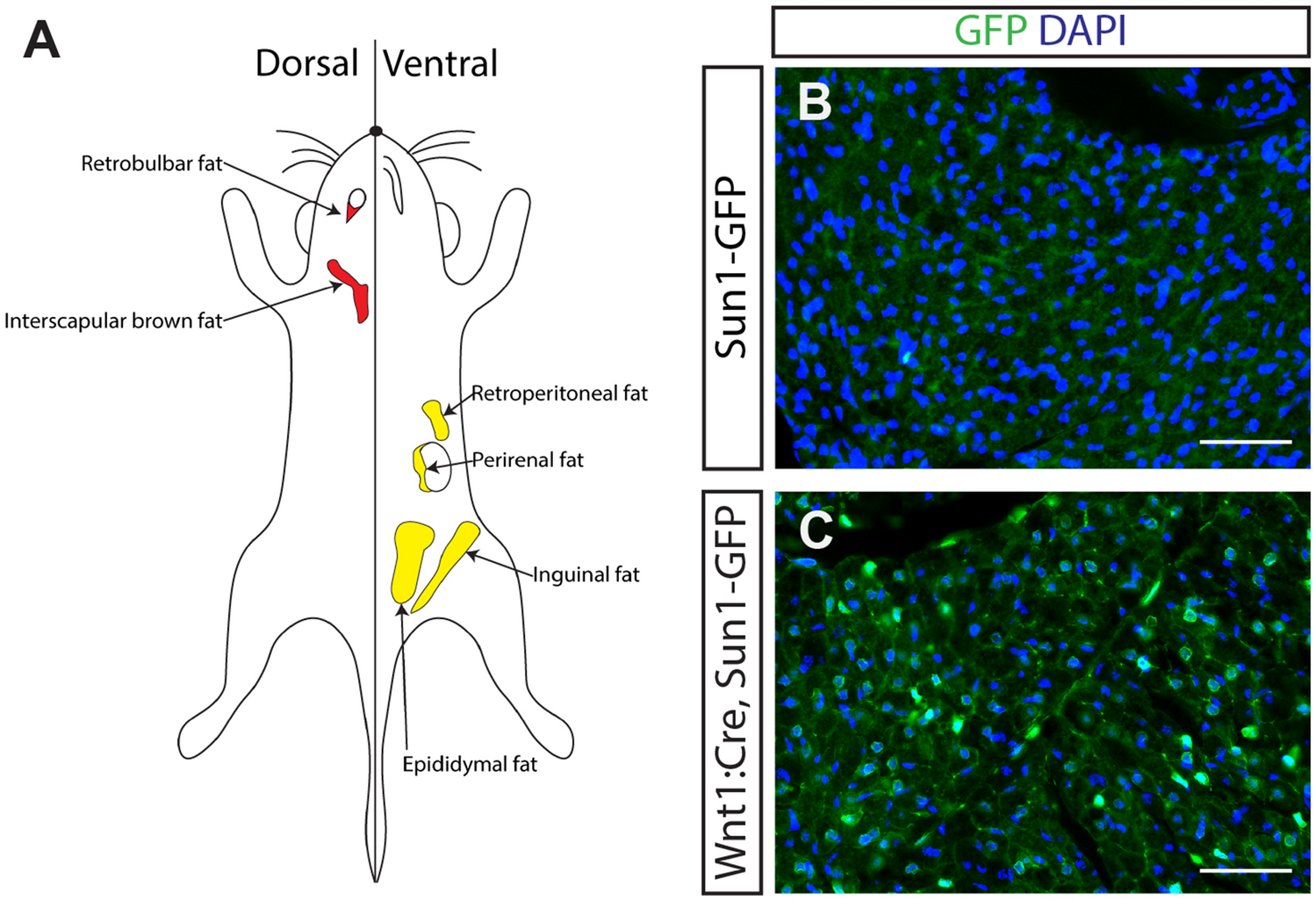
Temperature and species-dependent regulation of browning in retrobulbar fat
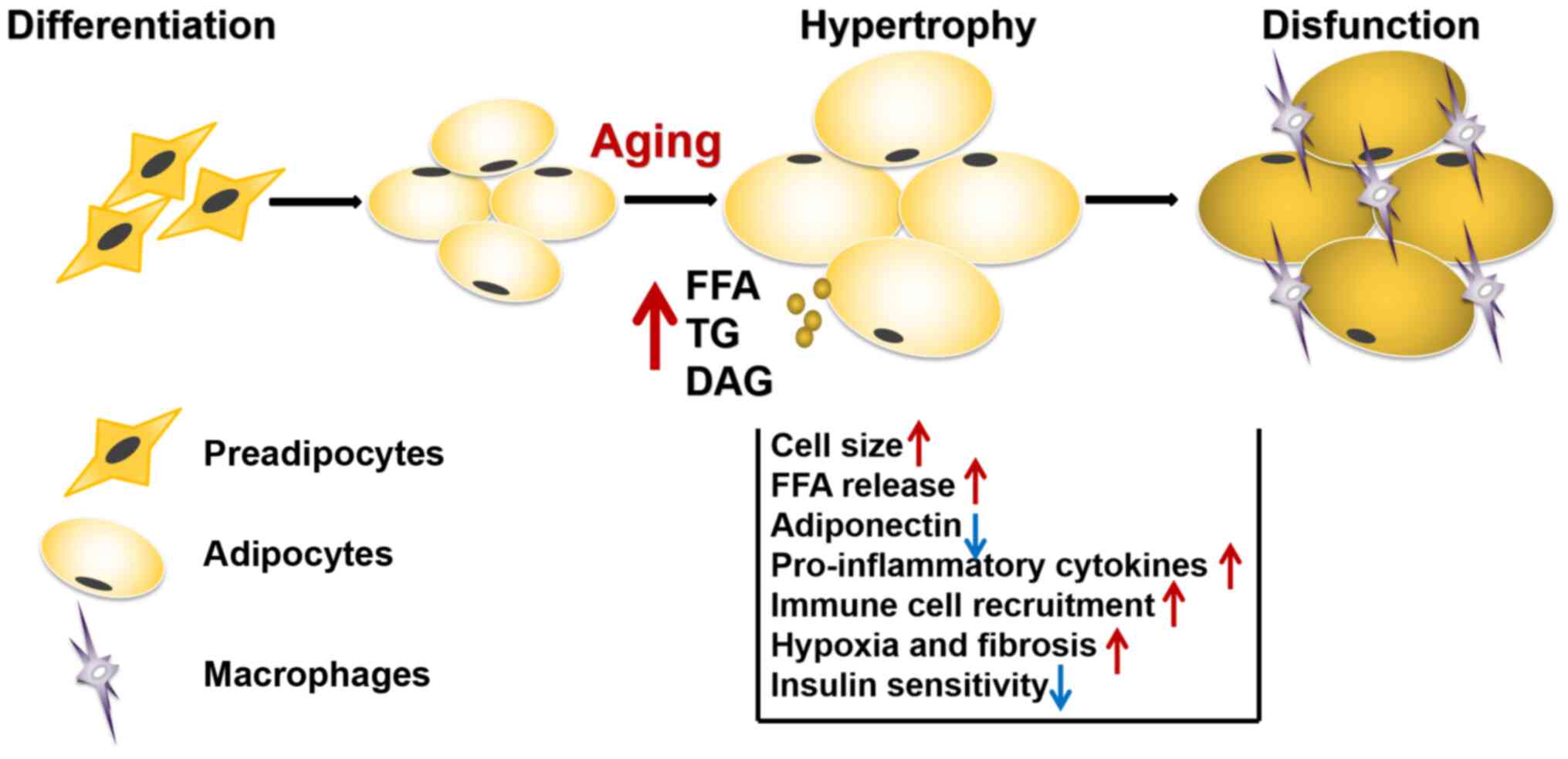
Adipose tissue and age‑dependent insulin resistance: New insights into WAT browning (Review)
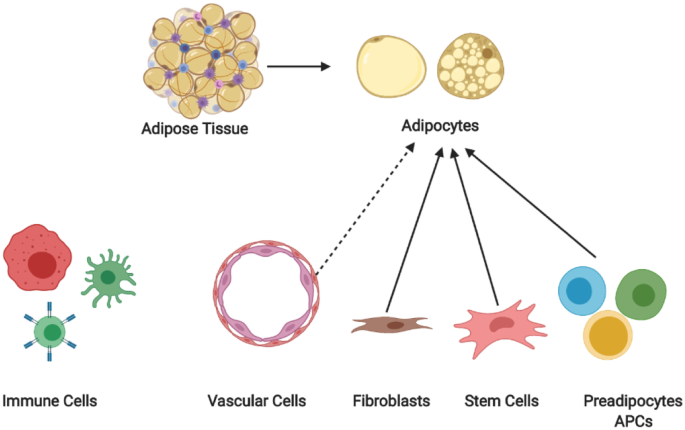
Novel insights into adipose tissue heterogeneity

New perspectives on the development of antiobesity drugs

New insights into PGC‐1 coactivators: redefining their role in the regulation of mitochondrial function and beyond - Villena - 2015 - The FEBS Journal - Wiley Online Library

The inter-organ regulation of adipose tissue browning. The schematic
Influenza A Virus Infection Induces White Adipose Tissue Browning: A Metabolic Adaptation to Infection?

Transcriptome and fatty-acid signatures of adipocyte hypertrophy and its non-invasive MR-based characterization in human adipose tissue - eBioMedicine

Defining the Human Adipose Tissue Proteome To Reveal Metabolic Alterations in Obesity

Adipose Tissue: Physiology to Metabolic Dysfunction - Endotext - NCBI Bookshelf

Locally Induced Adipose Tissue Browning by Microneedle Patch for Obesity Treatment
de
por adulto (o preço varia de acordo com o tamanho do grupo)







